

Science makes it known,
Engineering makes it work,
Art makes it beautiful.
This page is the next step after
Using Fujitsu COBOL 3.0 to call the USPS Address Matching System API; it is presumed that the reader is already
familiar with the compiling, linking, and Run-Time Environment Initialization
concepts discussed on that
The USPS ribbs site has been replaced, user will be redirected to current
This documentation only directly applies to Win32,
Fujitsu PowerCOBOL 3.0,
Fujitsu's COBOL 3.0 is a conventional 3rd generation COBOL85
Win32 programming
environment. Fujitsu's PowerCOBOL
is a graphical programming environment that allows
COBOL programmers to develop GUI applications with event-driven
structures. Fujitsu refers to the GUI application windows as sheets.
Using Fujitsu's
PowerCOBOL 3.0 Windows GUI capabilities with the
USPS Address Matching System API presented two challenges:
-
PowerCOBOL sheets calling COBOL subroutines, not C
and C++ functions (as in the AMS API), is documented. Also, ran
into problems using
non-default compiler options
NOALPHAL and DLOAD (see
Using Fujitsu COBOL 3.0 to call the USPS Address Matching System API for details)
for compiling PowerCOBOL sheets. (C++ is case sensitive;
by default COBOL is case insensitive, automatically makes all identifiers and
keywords
upper-case). According to the Fujitsu documentation, COBOL 3.0 programs can invoke both PowerCOBOL sheets and C++functions. As a workaround, use a COBOL 3.0 main program to serve as the unifying interface between PowerCOBOL sheets and the AMSAPI. In other words, the main program is a non-GUI COBOL 3.0 "wrapper" (alternatively, executive or dispatcher) program coordinating the calls between the PowerCOBOL sheets and the AMS API. -
Using COBOL 3.0 to invoke PowerCOBOL sheets. Could not
find within the Fujitsu documentation how to successfully link COBOL 3.0 main program
with PowerCOBOL
sheets. Necessary for above mentioned workaround.
The software design to meet challenge 1 can be summarized in the diagram below:

System Program Units:
(limited source code available for download below)
For this example, the main program is
AMSWIN
(a command console program). When executed, it
immediately displays the Main Menu PowerCOBOL sheet after initializing
Compiled with NOALPHAL (do not convert user-defined names'
lower case letters to upper-case), DLOAD (Dynamic Load), MAIN (main
program) options.
Subroutine to invoke PowerCOBOL sheets via the _POWEROPENSHEET
call (_POWEROPENSHEET is a
Fujitsu
001040 CALL "_POWEROPENSHEET" USING DLL-NAME
001050 SHEET-NAME.
DLL-NAME is the fully qualified file name of the .DLL file containing
the name of the PowerCOBOL sheet to be opened.
SHEET-NAME is the name of the PowerCOBOL sheet (GUI application window)
Compiled with ALPHAL, DLOAD, NOMAIN options.
(this is an earlier version of INVKSHT available at
COBOL Files - Combining Fujitsu COBOL 3.0, PowerCOBOL 3.0, Silverfrost FTN95, and Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing;
however, the values of DLL-NAME and SHEET-NAME are hard-coded in
both versions and therefore incompatible)
It should be noted that while the Fujitsu documentation recommends that
both the calling program and called program be compiled with the same compiler options,
it is not
Presents to user a menu of various functions to
manipulate, extract, or update mailing lists.
Some function to convert mailing lists from one format to another.
(not the focus of this discussion, shown for demonstration purpose only)
Another function to manipulate a mailing list..
(not the focus of this discussion, shown for demonstration purpose only)
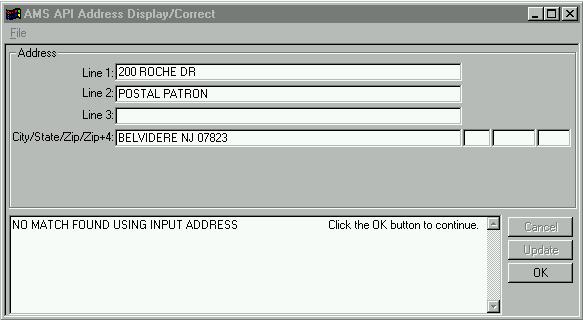
The central PowerCOBOL sheet for this discussion, shown below:

The sheet is used to
select a mailing list file, verify that it is a mailing list, and allows the user to select
one of three
This is an important support sheet for the Validate Mailing List
The purple arc in the
software design diagram above represents the flow.
PowerCOBOL sheets receive system data through a Fujitsu predefined
Linkage Section, precluding
parameter passing to the PowerCOBOL sheet with the USING clause of the
CALL
(The predefined Linkage Section serves a similar purpose as the
variable declaration in the C statement
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
or the D statement
extern (Windows) BOOL DllMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, ULONG ulReason, LPVOID pvReserved))
PowerCOBOL sheets compiled and linked using default options.
Common code used in more than one source code file. Usually used for
data declarations. In this application, some (not all) are used
as GLOBAL EXTERNAL
data declarations for passing data between main program and
PowerCOBOL 3.0 sheets.
USPS Developer's Kit containing
functions (dynamic link library ZIP4_W32.DLL)
for checking the integrity of an address, determining
ZIP+4,
and mailing list validation.
Linking:
The answer to challenge 2 (Using COBOL 3.0 to invoke PowerCOBOL sheets)
was relatively simple to

_POWEROPENSHEET must also be defined in the entry information section of the Run-Time Environment Initialization File COBOL85.CBR. This is the last line as shown below.
[AMSWIN]
@IconName=COB85EXE
@ScrnSize=(80,24)
@CnslWinSize=(80,24)
@CnslBufLine=100
@WinCloseMsg=ON
@EnvSetWindow=UNUSE
@AllFileExclusive=NO
@CBR_PrintTextPosition=TYPE1
@CBR_TextAlign=BOTTOM
[AMSWIN.ENTRY]
z4openSTD=ZIP4_W32.DLL
z4closeSTD=ZIP4_W32.DLL
z4adrinqSTD=ZIP4_W32.DLL
_POWEROPENSHEET=F5BBRUNS.DLL
ATTENTION:
When doing a Google Search for "COBOL AMS API" you may find several
references for Google Docs with the same terms and even graphics used in my
Fujitsu COBOL pages. THE Google Docs ARE NOT MINE. They may have
links for downloadable executable files which may or may not contain malware,
adware, or other undesirable features. Example addresses are:
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1eeXg8lPjGBtAdP7IfE5MdebjnEE8X0W3wAyEMWw1eLo/edit?pref=2&pli=1
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1pE3ESiOnkQoowG_XvLoZgxRSXDKnPQw2Drk4EBBe2gY/edit?pref=2&pli=1
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1mjzJ_6pWqFmacRxzD5Fg7Wy7zCjxTVleghVYGsJUaGY/edit?pref=2&pli=1
Exercise Caution


