

Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing - Simulated Annealing
(and other programming topics/tutorials)
This web site presents an implementation of Simulated Annealing using a hybrid software system of D and FORTRAN (D is one of the
newest programming languages, FORTRAN is one of the oldest). Site additionally covers other Numerical Recipes topics, as well as
Artificial Life, Model Rockets, Object Pascal, COBOL, etc. The source code files available for download on these pages can
be used as learning examples and as building blocks for writing your own applications; they are enhanced and bug tested
periodically - occasionally, as with any software project, minor glitches will sneak through. These are corrected and
uploaded as discovered. The projects on these pages employ software re-use extensively - one .dll may be used by
multiple projects written in several different programming languages.
Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing is a series of editions covering numerical computations, published by Press
Syndicate of the University of Cambridge. Over the years, editions have been published in the FORTRAN, Pascal, C (and other)
programming languages.
Simulated Annealing is one of the subjects covered in several editions of Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing.
Simulated Annealing, also known as the traveling salesman problem, is used for combinatorial minimization. The traveling salesman
problem involves a salesman who must travel to a large number of cities (or nodes, represented by X Y coordinates). What is the
shortest path the salesman can traverse visiting these cities? (What configuration produces the shortest distance, or lowest cost?)
In a very large 'solution space', there are some solutions that are 'low cost' (global minima) relative to other solutions. Simulated
annealing searches for these 'low cost' solutions. Simulated annealing has also been applied to designing integrated circuits.
|
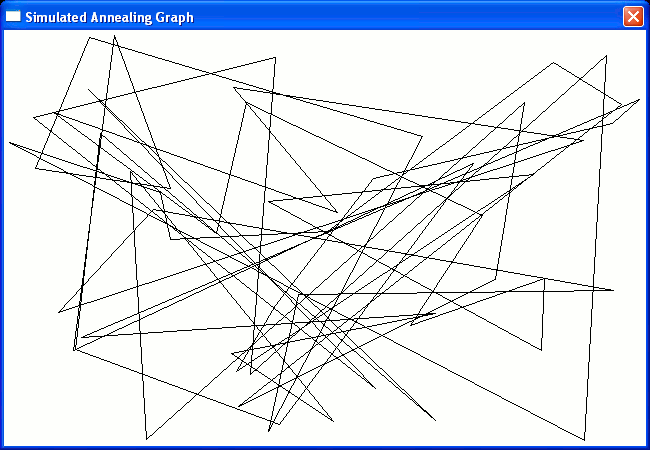
Traveling Salesman Itinerary before Simulated Annealing
Path produced by random x,y data points generated by procedure Plotted by function plotPoints (hGraph, hdc, lpPoint, nNodes, gx1, gx2, ix, gy1, gy2, iy, iOrder, grX, grY, WinNrmlAlgNrml) in D module dnrprocs. Both graphs and user interface (below right) are from wmath.exe (module wmath; source code wmath.d) From the user interface, command File, Anneal calls dANNEAL (...) in module dnrprocs. From the same user interface, command |
(module dnrprocs plotting procedures have been upgraded to include axis) |
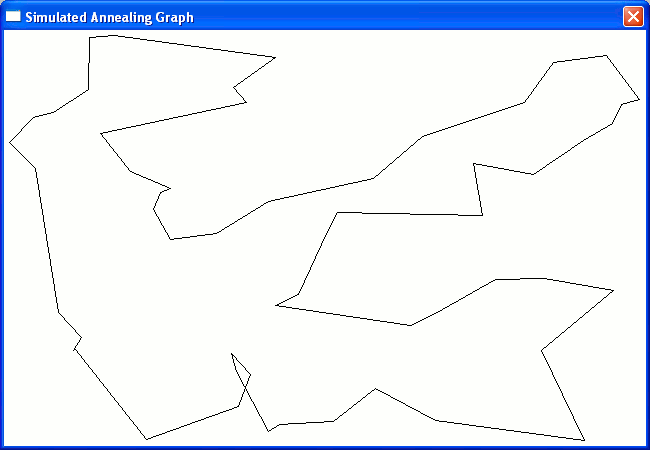
| Traveling Salesman Itinerary after Simulated Annealing
Same x,y data points reconfigured by simulated annealing procedure dANNEAL (nCity, x, y, mu, iOrder, path, eCost, iErr, IOflag, hWnd) in D module dnrprocs, resulting in a much shorter path. Plotted by function plotPoints (hGraph, hdc, lpPoint, nNodes, gx1, gx2, ix, gy1, gy2, iy, iOrder, grX, grY, WinNrmlAlgNrml) in D module dnrprocs. ViewGraph (hWnd) is an example of a |
 |
|
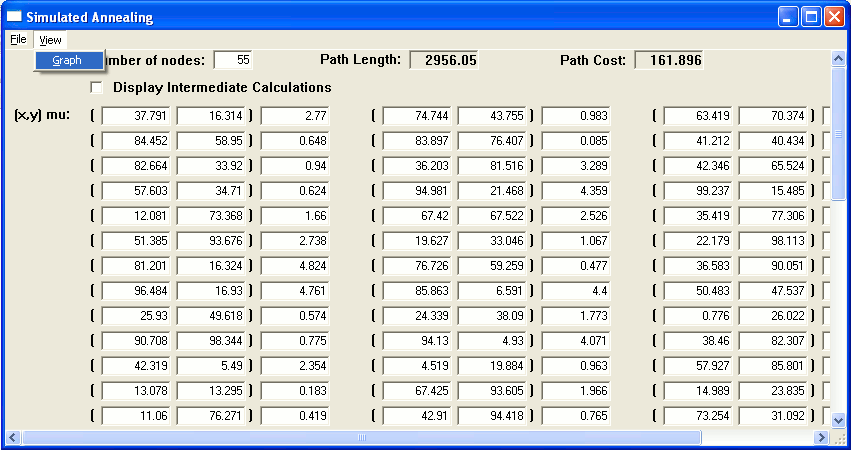
wmath.exe
User Interface more advanced and functional version of Simulated Annealing Demonstration Module wmath uses two windows and two windows callback procedures; one for the user interface at right, the other for displaying the simple graphs above right. Written in D. |
 Has rudimentary
Command Line Parameter Parser
(input file name, number of nodes). D module CmdLine.d calls
procedures in
Has rudimentary
Command Line Parameter Parser
(input file name, number of nodes). D module CmdLine.d calls
procedures in Calls module hedito function hEditPopUpMenu (...) for right click short cut popup menu for basic clipboard Cut, Copy, Paste, Delete, compile with: dmd wmath.d dnrprocs.lib sttstcs.lib cmdline.lib hedtio.lib hwndio.lib win.def [see DMD D .DLL calling FORTRAN .DLL (D file) (link below), Compiling/Linking, step 7, for information on win.def] |
The traveling salesman problem is a NP-Complete problem, where N equals the number of nodes (or cities), and the
computation time is proportional to eN.
DMD D .DLL calling FORTRAN .DLL (D file)
Simulated Annealing D .dll calling FORTRAN .dll; includes D source file downloads.
DMD D .DLL calling FORTRAN .DLL (FORTRAN file)
Simulated Annealing FORTRAN .dll (mathproc.dll) called by D module dnrprocs.dll. mathproc.dll is used in multiple projects.
XBCRANK.X
|
Source file containing port from FORTRAN to XBLite of Numerical Recipes'
subprogram CRANK (...) (returns array of ranks of
an input integer array). Also has generic text to numeric conversion utility
(can handle decimal, hexadecimal, and octal formats), Windows API child
create (has been successfully called from a D Windows
program) & I/O |
|
Structure and Elements of a FORTRAN Program
Layout, keywords, specification statements, and executable statements of a FORTRAN program.
Additional subprograms in mathproc.dll
Miscellaneous FORTRAN Mathematical Subprograms - point rotation, triangular segment area, polynomial roots,
synthetic division.
Additional Programming Topics
D/Object Pascal/Lazarus/FORTRAN Mixed Language programmingFree Pascal calling FORTRAN subprograms in mathproc.dll
Describes how to use Pascal to call FORTRAN Mathematical Subprograms
Lazarus, Free Pascal, Silverfrost FTN95, and Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing
Lazarus Program (via a Free Pascal .dll) calling FORTRAN subprograms.
Simple D program to call Pascal .dll - D files
Describes how to use a D simple command program to call Pascal functions in a Pascal .dll; using D extern statements,
passing parameters, compiling and linking.
D Programming Language, Silverfrost Fortran 95, and Numerical Recipes
How to call FORTRAN subroutines using a simple command line Digital Mars D main program.
Pascal .dll called by simple D program
Pascal functions called by D simple command program
Silverfrost Fortran 95 subroutine to compute Nth Root of X
FORTRAN function (including source code) to compute
Artificial Life, Strange Attractors, & Bifurcations (D & Object Pascal)
- Artificial Life - life-like patterns emerging in cellular automata and related arrays.
- Strange Attractors - An attractor of a chaotic system, the exact
behavior in the system never repeats; demonstrates
sensitive dependence on initial conditions; fractal structure. - Bifurcations - emergence of a new attractor(s) in a dynamic, complex
system that occurs when some parameter reaches
a critical threshold value
| Dawkins8 Biomorph
(Artificial Life) (Tree Height : 60; Branch Data produced by procedure DAWKINS (hWindow, hEditOutput, ix, iy, alpha, treeHeight, branchAngle, branchLength, biQuadSymtryInd, nPts, iErr) in Object Pascal Library dawkins8.dll (callable by both D and Pascal Windows main programs; Pascal version also demonstrates appending text to a windows edit control) Lines plotted by function plotLines2 (hGraph, hdc, &Point, n, gx1, gx2, ix, gy1, gy2, iy, grX, grY, WinNrmlAlgNrml) in D module dnrprocs. |
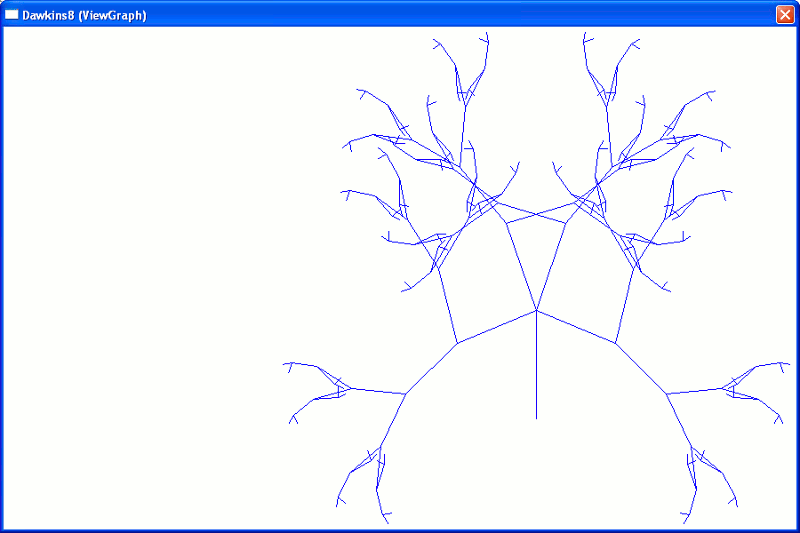
Include file genetyp.inc, Object Pascal Librarys genecode.pas and dawkins8.pas are major rewrites from Rietman, Edward (1994) Genesis Redux: Experiments Creating Artificial Life; unfortunately, to prevent any intellectual property violations, neither genecode.pas or dawkins8.pas are available for download from this site. Called by wlife.d main program (uses two windows and two windows callback procedures, similar to wmath.d above); also demonstrates creating Windows Tool Tips via calls to CreateToolTip (...) in D module hedtio. |
| D module alife
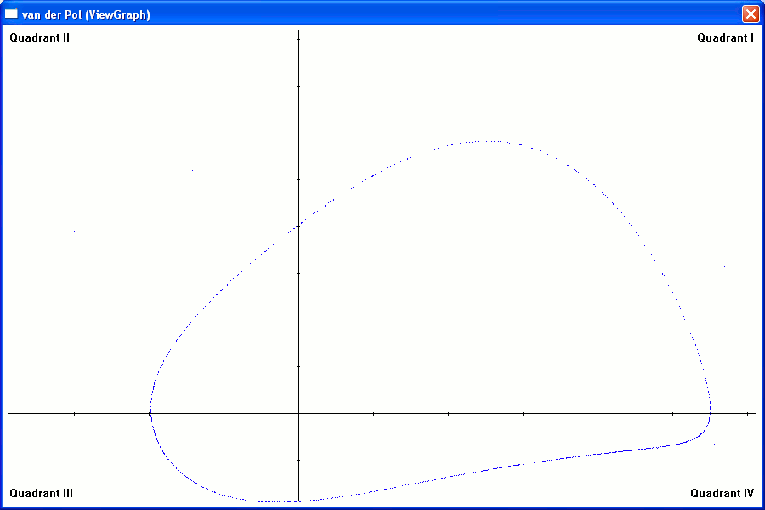
(Strange Attractors & Bifurcations) Port of several stand-alone GW-BASIC programs from E. Rietman (1993) Creating Artificial Life : Self-Organization to D .dll alife.d : Artificial Life D source file, compiles into .dll. Includes Brusselator limit cycle, Iterated Map, Phase Diagram, Rayleigh, Rossler, and van der Pol equation. Requires module dnrprocs. alife.di : D Interface file compile with: dmd -c alife.d -g dmd alife.obj alife.def -g van der Pol equation (nonlinear electric circuit) plot produced by module dnrprocs function plotPixels(hGraph, hdc, rgb, n, gx1, gx2, ix, gy1, gy2, iy, grX, grY, WinNrmlAlgNrml) Called by main D module wlife (see above). |
 Uses D module CmdLine.d for Command Line Parameter Parsing
Uses D module CmdLine.d for Command Line Parameter Parsing
Compile and link D module wlife with: dmd wlife.d alife.lib dnrprocs.lib hedtio.lib CmdLine.lib dawkins8.lib win.def |
|
Lazarus, Pascal, FORTRAN, D, and Model Rockets
Several components of a software system to input and analyze a While researching Drag Coefficients, came across both MODEL ROCKET SIMULATION WITH DRAG ANALYSIS |

|
Unit MRcommon.pas (currently still in development), consisting of Global CONSTants, VARiables (many of which are passed to various Pascal procedures/functions, which in turn may pass to FORTRAN subprograms), and Public Procedures, is used in all of the Lazarus Model Rockets & Boost/Gliders Units.
Calculating Model Rocket Coefficient of Normal Force & Center of Pressure
mathproc.dll FORTRAN Engineering Subprograms called by Object Pascal .dll; introduction to rocket aerodynamics & stability;
includes source file downloads - tir33.for, missle.inc, missle02.pas. missle02.pas includes a Pascal implementation of
ELLIPSE_SEGMENT algorithm from CALCULATING ELLIPSE OVERLAP AREAS, used for finding the surface area of a
rear swept elliptical fin/wing where the root chord does not pass through the ellipse origin. Elliptical area / perimeter calculations can
be complex, involving geometric angles, parametric angles, integrations. Both the unswept/swept elliptical fins/wings area and
perimeter calculations are approximations.
Multi-Stage Model Rocket User Interface
Using Lazarus Tab Sheets (TPageControl & TTabSheet) tutorial; each Tab Sheet represents a model rocket stage. Brief introduction
to Lazarus sub-forms. User interface for inputting rocket design parameters and Calculating Model Rocket Coefficient of Normal Force & Center of Pressure (link above).
Lazarus Body Tubes Sub-form User Interface
Lazarus Sub-form, Grid Cell Background Color, StringGrid Cell Editor, and Calling FORTRAN. Detailed introduction to Lazarus
sub-forms and TStringGrids; example of Lazarus unit calling FORTRAN subprograms via Object Pascal .dll; includes downloads.
Lazarus Model Rocket Fins and Glider Wings User Interface
Lazarus Sub-form, TImage.Picture property, MessageDlg(...),
(MRmain for
This form is used for input of flight surfaces data. Another example of calling FORTRAN from Lazarus via Object Pascal.
Includes downloads.
Model Rocket Parallel Stages
Lazarus Sub-form user interface for inputting Parallel Stage data and adding Parallel Stage Pods to a rocket's nth stage. Also
demonstrates calling FORTRAN mathproc.dll Center of Pressure cp and Coefficient of Normal Force CNα subroutines from Lazarus
via an Object Pascal Library; includes downloads, compiling instructions (including brief hints for building sttstcs.for
& mathproc.for, main Lazarus project MRmain).
Model Rocket & Boost/Glider Drag Coefficient Approximation
D Windows 'testing' program (still in development) to estimate Drag Coefficient for model rockets, parallel stages, boost/gliders, and rocket/gliders. Run time edit control creation.
Engine Thrust File I/O - missle05.pas
Object Pascal Windows program to input and save to a file thrust points from a model rocket engine thrust time curve. Requires
missle.inc and missle02.pas from Calculating Model Rocket Coefficient of Normal Force, uses unit missle06 to write thrust points file;
Lazarus programs can call a .dll (missle13.pas; also contains Parallel Stage Pod and Drag Coefficient procedures; portions still being
developed) which uses missle06.pas. Demonstrates how to call D procedures using its mangled name or its unmangled name when
declared as extern (C), right click short cut popup menu processing via calls to D module hedtio.
Requires additional source files found elsewhere on this website.
LftBdy10.pas - Lifting Body related functions/procedures. Currently in development.
COBOL Program Structure and Elements
Structure, keywords, data definition, and executable statements of a COBOL program
COBOL Files - Combining Fujitsu COBOL 3.0, PowerCOBOL 3.0, Silverfrost FTN95, and Numerical Recipes
COBOL GUI program calling FORTRAN Subprograms : The COBOL "wrapper" - source files, compiling, and linking.
FORTRAN File - Combining Fujitsu COBOL 3.0, PowerCOBOL 3.0, Silverfrost FTN95, and Numerical Recipes
A FORTRAN backend used by COBOL, Lazarus, and D programs
Selected Combining Fujitsu COBOL 3.0, PowerCOBOL 3.0, and the USPS Address Matching System API source files:
INVKSHT.COB - invokes PowerCOBOL sheets
USPSFILE.COB - mailing list input file Select Assign statement. Placed in ENVIRONMENT DIVISION, INPUT-OUTPUT SECTION,
FILE-CONTROL.
USPSLIST.COB - mailing list input File Descriptor and record layout. Placed in DATA DIVISION, FILE SECTION. Record layout is
designed so it can be used with several different mailing list input formats.
OUTFILE.COB - output file Select Assign statement. Placed in ENVIRONMENT DIVISION, INPUT-OUTPUT SECTION,
FILE-CONTROL.
OUTREC.COB - output File Descriptor and record layout. Placed in DATA DIVISION, FILE SECTION. Record layout is designed
so it can be used with several different mailing list input/output formats.
Z4GBLPRM.COB - AMS API Common Data used by above.
Privacy : Some thoughts on privacy during the computer
|
Primary Site:
|
Linked In Public Profile:
|
| Web hosting provided by | 
|
Any and all © copyrights, ™ trademarks, or other intellectual property (IP) mentioned here are the property of their respective owners.
No infringment is intended. Feel free to use any of my material; please give credit (same idea as Copyleft).
Currently moving some pages from one host to another; some links may be temporarily broken. Depending on O/S, Browser (and plugins), Browser may not correctly include L/F. Rest assured, both issues will be corrected.
Website is supported on DESKTOP platforms only (Chrome on both PCs and Android tablets may be problematic). This index page is an "alternate" main page to selected pages of author's website, focusing on different areas.
To return to this index page, use the Browser's BACK button.
The author of this web site is not affiliated in any way with Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge.